SCM Nano Diamond
About SCM Nano Diamonds
Dia Material develops diamond particles with an average particle size of less than 100 nm (0.1 µ) as ultrafine (nano) diamonds.
As a domestic manufacturer, we pursue a stable supply of nanodiamonds while actively conducting joint research with various industries to develop new applications.

| Types of nano-diamonds (ultrafine diamonds) handled (origin of production method) |
|
| Polycrystalline (impact compression) |
Monocrystalline (static pressure) |
Diamond Properties
Hardness, low friction, high thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion, wide gap, stability, surface properties, etc.
Application development
Ultra-precision polishing, solid-state sliding, plating, heat sinks, CVD seed crystals, electron emission, UV blocking, catalysis, adsorption, medical, etc.
Physical properties of nanodiamonds
Polycrystalline type
100nm, FE-SEM x100,000 times

100nm, TEM x80,000 times
Secondary particles can be classified in 50 nm intervals
Residual impurities inside the sintered body (<1%)
Monocrystalline type
100nm, FE-SEM x100,000 times
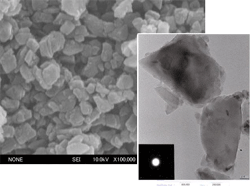
100nm, TEM x80,000 times
(Static pressure method, 50,000 atmospheres, 1,200°C x approx. 10 min)
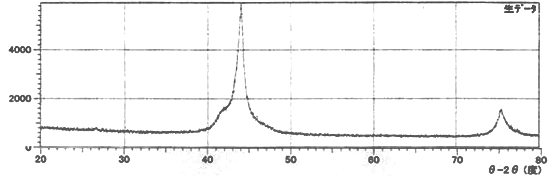
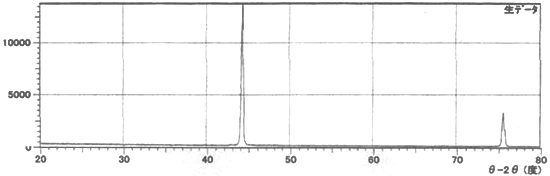
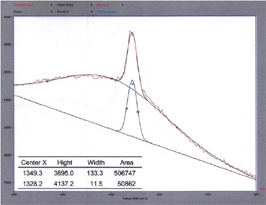
X-ray diffraction chart of nanodiamonds
Various diamonds (grain size 100 nm) Powder X-ray diffraction results
| Polycrystalline | Monocrystalline | UDD type |
|---|---|---|
| CUB/HEX | CUB | CUB |
| FWHM1.2-1.8 | FWHM0.4-0.6 | FWHM1.7-2.2 |
| Particle size 10-20nm | - | Particle size 3-8nm |
Polycrystalline
Monocrystalline
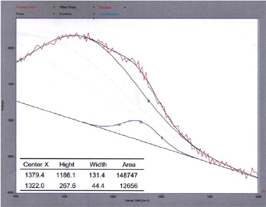
Examples of Raman spectroscopy
measurements of nanodiamonds
Crystallinity (1330 cm-1): single crystal > UDD type > polycrystalline
In cluster diamonds, a non-diamond carbon peak (sp2 carbon) is often identified around 1580 cm-1.
Polycrystalline type
Monocrystalline type
Handling of
nanodiamonds: classification
Polycrystalline type
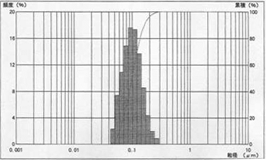
100nm d50=0.0991μ, mv=0.1065μ, s.d. 0.0385
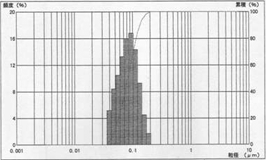
80nm d50=0.0828μ, mv=0.0874μ, s.d. 0.0338
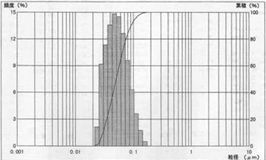
50nm d50=0.0505μ, mv=0.0562μ, s.d. 0.023
Products for conventional applications are available in the abrasives market.
Samples are available for other applications and for sub 50nm applications.
Tested by MicrotracUPA
Monocrystalline type
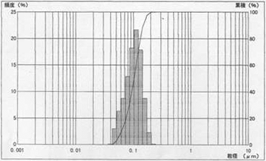
100nm d50=0.1028μ, mv=0.1041μ, s.d. 0.0344
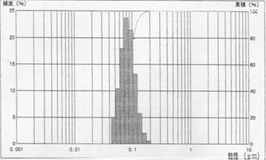
80nm d50=0.0815μ, mv=0.0852μ, s.d. 0.0244
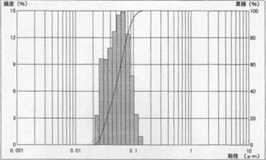
50nm d50=0.0536μ, mv=0.0589μ, s.d. 0.0246
Products for conventional applications are available in the abrasives market.
Samples are available for other applications and for sub 50nm applications.
Tested by MicrotracUPA
